Charting and technical analysis involve analyzing price charts to predict market movements by identifying patterns and trends. This approach helps traders make informed decisions.
1.1 Overview of Charting and Technical Analysis
Charting and technical analysis are methods used by traders to predict market movements by analyzing past price data. They involve identifying patterns‚ trends‚ and signals in price charts to forecast future price behavior. Technical analysis focuses on market psychology‚ using tools like charts and indicators to guide trading decisions effectively.
1.2 Importance of Charting in Financial Markets
Charting is crucial for predicting market movements and making informed trading decisions. By analyzing price trends‚ support/resistance levels‚ and indicators‚ traders can identify opportunities and risks. It complements fundamental analysis‚ offering a visual and data-driven approach to understanding market psychology and behavior in financial markets.
Key Concepts in Technical Analysis
Key concepts in technical analysis include price action‚ trends‚ support/resistance‚ volume‚ and indicators. These tools help traders interpret market psychology and make informed decisions.
2.1 Understanding Price Action and Trends
Price action reflects market psychology‚ showing how buyers and sellers interact. Trends indicate market direction‚ categorized as uptrend‚ downtrend‚ or sideways. Understanding these helps traders predict future movements and identify potential entry or exit points effectively.
2.2 Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels are where buying interest is strong enough to prevent further price declines. Resistance levels are where selling pressure halts upward movements. These levels are crucial for identifying potential market reversals and confirming trends‚ helping traders make informed decisions.
2.3 Volume and Its Role in Technical Analysis
Volume measures the number of shares or contracts traded‚ confirming the strength of price movements. High volume often validates trends and breakouts‚ while low volume may indicate weakness. It is a critical component in technical analysis‚ helping traders assess market sentiment and identify potential trading opportunities.
Common Technical Indicators
Common technical indicators help traders identify trends‚ confirm patterns‚ and make informed decisions‚ enhancing their market analysis and improving trading strategy effectiveness.
3.1 Moving Averages (MA)
Moving Averages (MA) are trend-following indicators that smooth price action by averaging historical prices over a set period. They help identify trends‚ signal potential reversals‚ and provide support or resistance levels‚ making them essential tools for traders in technical analysis to filter out market noise and focus on the broader trend.
3.2 Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the magnitude of recent price changes to determine overbought or oversold conditions. It ranges from 0 to 100‚ with levels above 70 indicating overbought and below 30 oversold. Traders use RSI to identify potential reversals and confirm trend strength‚ aiding in buy or sell decisions effectively.
3.3 Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a volatility indicator consisting of a moving average and two standard deviations. They help identify market volatility‚ overbought/oversold conditions‚ and potential breakouts or reversals‚ aiding traders in making informed decisions with precise entry and exit strategies.
Chart Patterns in Technical Analysis
Chart patterns help predict price movements by identifying shapes like head and shoulders or triangles‚ signaling potential trend reversals or continuations‚ aiding traders in strategic decision-making.
4.1 Reversal Patterns (Head and Shoulders‚ Double Tops)
Reversal patterns like the head and shoulders and double tops signal potential trend changes. The head and shoulders pattern forms with a peak followed by a higher peak and a lower peak‚ indicating a reversal. Double tops show two failed attempts to break a resistance level‚ signaling downward momentum.
4.2 Continuation Patterns (Triangles‚ Flags)
Continuation patterns‚ such as triangles and flags‚ indicate a pause before the trend resumes. Triangles form with converging support and resistance lines‚ signaling a buildup of energy. Flags appear as channels with parallel lines‚ often after a strong move‚ suggesting a continuation of the trend once broken. These patterns help traders anticipate trend resumptions.
4.3 Breakout and Fakeout Patterns
Breakout patterns occur when price surpasses resistance or support levels‚ signaling trend continuation. Fakeouts mimic breakouts but reverse sharply‚ trapping traders. These patterns help identify potential trend reversals or continuations‚ requiring careful confirmation to avoid false signals and manage risk effectively in trading decisions.

Practical Application of Technical Analysis
This section explores how traders apply technical analysis tools to identify opportunities‚ manage risks‚ and execute trades effectively using indicators and patterns in real markets.
5.1 Using Indicators to Identify Trading Opportunities
Traders use indicators like RSI‚ MA‚ and Bollinger Bands to identify overbought/oversold conditions‚ trend reversals‚ and volatility. These tools help spot potential entry/exit points‚ optimizing trading decisions and maximizing profitability in dynamic markets.
5.2 Combining Chart Patterns with Indicators
Combining chart patterns with indicators enhances trading strategies by confirming potential signals. For example‚ a head-and-shoulders pattern paired with RSI divergence strengthens reversal signals‚ while trendlines with moving averages refine entry/exit points‚ improving accuracy and confidence in trading decisions.
5.3 Risk Management in Technical Trading
Risk management is crucial in technical trading to protect capital and maximize returns. Using stop-loss orders‚ position sizing‚ and portfolio diversification helps mitigate risks. These strategies ensure disciplined trading‚ allowing traders to navigate market volatility effectively and sustain long-term profitability.
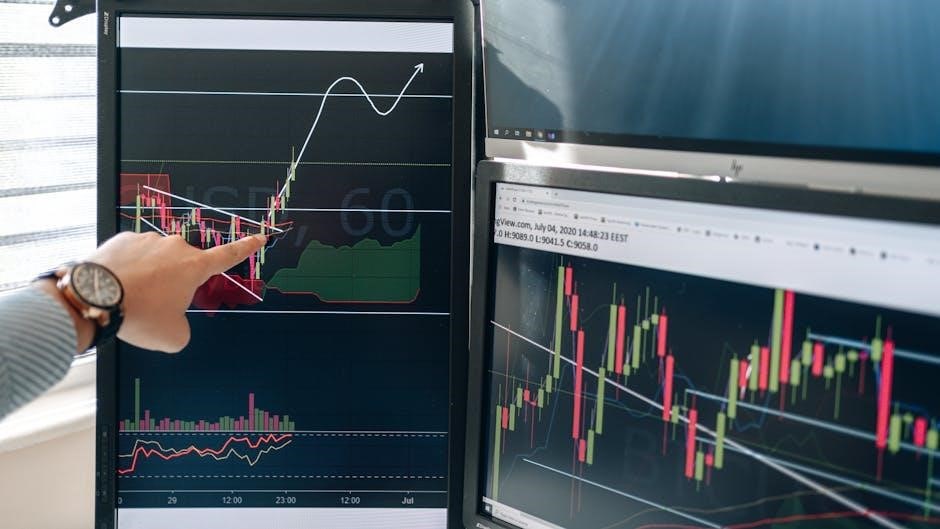
Advanced Techniques in Charting
Advanced charting techniques include Fibonacci retracement‚ Elliot Wave Theory‚ and candlestick patterns. These tools help traders identify complex market trends and make precise trading decisions effectively.
6.1 Fibonacci Retracement Levels
Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines indicating where support or resistance may occur. Derived from the Fibonacci sequence‚ these levels (23.6%‚ 38.2%‚ 50%‚ 61.8%‚ and 76.4%) help traders predict potential price reversals or pauses in trends‚ offering strategic entry or exit points.
6.2 Elliot Wave Theory
Elliott Wave Theory is a method for predicting market movements by identifying patterns in crowd behavior. Markets move in a series of waves—five upward and three downward—reflecting investor psychology. This theory helps traders anticipate potential trend reversals and price targets based on these repetitive patterns.
6.3 Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns are graphical representations of price action used to predict market movements. They reveal trader sentiment through shapes like Hammer‚ Shooting Star‚ and Engulfing. Each pattern reflects buyer or seller dominance‚ helping traders identify potential trend reversals or continuations. Mastery of these patterns enhances trading decisions and market insights.
Volume and Volatility Analysis
Volume and volatility analysis helps traders gauge market activity and risk. Volume confirms trends‚ while volatility measures price fluctuations‚ aiding in strategic decision-making and risk management.
7.1 Interpreting Volume in Price Movements
Volume is a key metric in technical analysis‚ reflecting market activity. High volume often confirms price trends‚ while low volume may signal uncertainty or weakness. Analyzing volume helps traders identify strong breakouts‚ reversals‚ and consolidations‚ providing insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
7.2 Understanding Volatility and Its Impact
Volatility measures price fluctuations‚ indicating market uncertainty. High volatility suggests rapid price swings‚ while low volatility reflects stability. Traders use indicators like Bollinger Bands or RSI to gauge volatility‚ helping them assess risk and identify potential trading opportunities or threats in dynamic markets.
7.3 Using Volume to Confirm Trends
Volume confirms trend strength by validating price movements. Rising prices with increasing volume indicate strong buying pressure‚ reinforcing uptrends. Conversely‚ falling prices with high volume highlight selling pressure‚ supporting downtrends. Decreasing volume during a price movement may signal weakening momentum‚ while low volume can lead to false breakouts‚ aiding traders in making informed decisions.
Combining Technical Analysis with Other Methods
Integrating technical analysis with fundamental analysis‚ sentiment analysis‚ and economic indicators enhances trading strategies‚ providing a holistic view of market dynamics and improving decision-making accuracy.
8.1 Integration with Fundamental Analysis
Combining technical analysis with fundamental analysis provides a comprehensive market view. Fundamental analysis assesses a company’s financial health through earnings reports and economic data‚ while technical analysis identifies price patterns and trends. This integration helps traders confirm trends‚ identify opportunities‚ and manage risks more effectively by blending quantitative and qualitative insights;
8.2 Using Sentiment Analysis with Technical Tools
Sentiment analysis complements technical tools by gauging market emotions through news‚ social media‚ and sentiment indicators. This integration helps traders identify potential price movements driven by fear‚ greed‚ or optimism‚ enhancing decision-making by combining emotional insights with technical signals for a holistic trading strategy.
8.3 Incorporating Economic Indicators
Economic indicators like GDP‚ employment data‚ and interest rates provide insights into market trends. Incorporating these into technical analysis helps traders anticipate sentiment shifts‚ confirm signals‚ and refine strategies for informed‚ data-driven decisions in dynamic financial markets.

Tools and Resources for Charting
Tools and resources for charting are essential for traders to analyze markets effectively. Popular platforms include Chartink‚ TradingView‚ and MetaTrader. Additionally‚ custom scanners and educational tutorials enhance trading strategies.
9.1 Popular Charting Software and Platforms
Popular charting software includes TradingView‚ MetaTrader‚ and Chartink. These platforms offer real-time data‚ customizable charts‚ and technical indicators. TradingView is known for its advanced tools and social features‚ while MetaTrader is widely used for automated trading. Chartink allows users to create custom scans and strategies‚ making them essential for technical analysis.
9.2 Custom Indicators and Scanners
Custom indicators and scanners allow traders to create tailored tools for specific strategies. These tools can automate pattern detection‚ enabling quick identification of trading opportunities. Advanced platforms offer customization options‚ letting users define criteria for scanning large datasets efficiently‚ enhancing their ability to make informed trading decisions.
9.3 Mobile Apps for Technical Analysis
Mobile apps for technical analysis provide traders with on-the-go access to real-time data and essential tools. Apps offer customizable charts‚ alerts‚ and indicators‚ enabling seamless trading decisions. Popular platforms support iOS and Android‚ ensuring traders can stay connected to markets and analyze trends anytime‚ anywhere‚ with advanced features for optimal performance.
Learning and Practicing Technical Analysis
Mastering technical analysis requires education and practice. Start with resources like “The Only Technical Analysis Book You Will Ever Need” and tools like Charting and Technical Analysis by Fred McAllen.
10.1 Tips for Beginners in Charting
Beginners should start with basic chart types like line and candlestick charts. Focus on major time frames and avoid overcomplicating analysis. Practice with historical data to identify patterns and trends. Use educational resources like “The Only Technical Analysis Book You Will Ever Need” to build a strong foundation.
10.2 Practicing with Historical Data
Practicing with historical data helps refine chart-reading skills and identify patterns. Start with major time frames to avoid confusion. Use backtesting to evaluate strategies and learn from past market behaviors. This hands-on approach builds confidence and improves decision-making abilities for traders at all levels.
10.3 Joining Trading Communities
Joining trading communities connects you with experienced traders‚ fostering knowledge sharing and support. Engage in discussions‚ access resources‚ and learn from real-world examples. These communities help refine strategies‚ build confidence‚ and stay updated on market trends‚ enhancing your technical analysis skills and overall trading journey.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Explore practical examples of successful trades and lessons learned from failed ones. Real-world case studies provide insights into applying technical analysis across diverse markets and timeframes effectively.
11.1 Successful Trades Using Technical Analysis
Discover how traders achieved profitable outcomes by applying technical analysis. Case studies reveal the use of indicators like RSI‚ Moving Averages‚ and Bollinger Bands to identify trends and patterns. Learn from real-world examples of successful trades and understand how to replicate these strategies in different market conditions and timeframes effectively.
11.2 Lessons from Failed Trades
Failed trades highlight common pitfalls in technical analysis‚ such as over-reliance on indicators or ignoring volume and volatility. Analyzing these mistakes reveals the importance of combining chart patterns with risk management and avoiding emotional decision-making; Learning from these errors enhances trading strategies and improves future outcomes significantly.
11.3 Applying Technical Analysis in Different Markets
Technical analysis is versatile across markets‚ including stocks‚ options‚ forex‚ and cryptocurrencies. While core principles remain consistent‚ adapting strategies to each market’s unique characteristics is crucial. Traders must consider volatility‚ liquidity‚ and market structure to effectively apply indicators and patterns‚ ensuring tailored approaches for optimal results in diverse financial environments.
Mastering charting and technical analysis requires practice and dedication. For further learning‚ explore books like “The Only Technical Analysis Book You Will Ever Need” and online resources for advanced strategies and tools.
12.1 Recap of Key Concepts
Charting and technical analysis involve studying price patterns‚ trends‚ and indicators to predict market movements. Key concepts include trend identification‚ support/resistance levels‚ volume analysis‚ and indicators like RSI and Bollinger Bands. These tools help traders make informed decisions and identify potential trading opportunities while managing risk effectively.
12.2 Recommended Books and Resources
Essential books include “The Only Technical Analysis Book You Will Ever Need” and “Charting and Technical Analysis” by Fred McAllen. Online platforms like TradingView and Investopedia offer valuable tools and tutorials. Additionally‚ resources such as StockCharts and Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets by John J. Murphy are highly recommended for deeper insights.
12.3 The Future of Charting and Technical Analysis
The future of charting and technical analysis lies in AI-driven tools and machine learning algorithms enhancing predictive capabilities. Integration with big data and real-time analytics will refine decision-making. Mobile apps and cloud-based platforms are expected to make these tools more accessible to a broader range of traders and investors globally.
